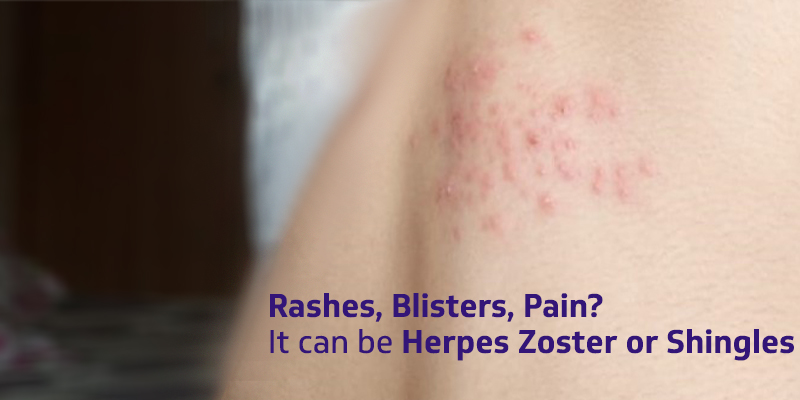
Doctors are seeing many patients with Herpes infection these days. Although this infection is more common in summers but this year it is on a rise in winters too. Patient usually approaches the doctor with some red skin rashes, boils or blisters along with pain. These rashes can occur in any part of the body but they are most commonly seen on face, neck or on one side of your torso.
What causes Herpes infection?
Herpes is also known as Shingles. It is caused by a virus called Varicella-Zoster virus, which is the same virus that causes Chicken pox. So, if you got chicken pox infection in your childhood, even after recovering, this virus remains dormant in your body for very long time and when it is reactivated, it leads to Shingles.
Shingles usually lasts for 3 to 5 weeks. It starts with pain, burning or tingling sensation on the skin. Within 4 – 5 days a red rash appears with fluid-filled blisters. You may also experience cold- like symptoms such as headache, fever or tiredness. During the next 10-15 days the blisters dry up and form scabs which clear up within few weeks. Some people may experience pain even after the blisters are gone.
What are the symptoms of Herpes Zoster?
In the beginning you may experience pain and burning on one side of the body, which is followed by the appearance of rashes. Features of rash may include:
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Red patches
- Common on face and ears
- Burning and itching sensation
Some people may also experience:
- Chills
- Headache
- Fever
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
The first symptom of Herpes Zoster is pain and it can be severe in some cases. The rash which develops later usually constitutes of stripe of blisters that wrap around on one side of the torso. It may also occur around one eye or on one side of the face or neck.
Can Shingles spread?
No, Shingles cannot spread from one person to other. It is non-contagious condition. However, it can spread to another person who did not have chicken pox in their life and cause chicken pox in that person.
Who can get Shingles?
Anyone who had chickenpox in childhood can get Shingles. Factors that increase the risk of getting Shingles may include:
- Risk of infection increases with age. It is most common after the age 50
- Mental stress
- Conditions that weaken your immunity, can increase the risk of Shingles like AIDS, Cancer, Diabetes etc
- Prolonged use of steroids can also increase the risk of Shingles
Are there any complications?
Complications are rare and may include:
- Pain or rash involving the eye can cause permanent eye damage or vision loss
- Loss of hearing
- Intense pain in one ear
- Facial paralysis
- Loss of taste
- Bacterial skin infections
- Postherpetic neuralgia: You may experience pain even after the blisters have cleared
What is the treatment?
There is no exact treatment for Shingles however prompt management with antiviral medicines can speed up the recovery and reduce the risk of complications. It is best to start the treatment within 72 hrs of developing the symptoms.
If you have noticed some red rash on your body and it is causing pain and discomfort, you should meet a physician or a Dermatologist at RxDx Multispecialty Clinic. They will examine the rash and your health status and then advice you best possible treatment.
Compiled By,
Dr Manjari Bansal– Content Writer, RxDx
For further details, please contact: 080-49261111, 6745-8111

