Echocardiography
2D / 3D / 4D / Doppler Echo
4D Advanced Cardiac Imaging at RxDx Clinics, Whitefield
Experience next-generation precision in heart diagnostics at RxDx. With the addition of the GE Vivid E95 Ultra Edition, we bring world-class 4D echocardiography and advanced cardiac imaging to your neighbourhood in Bengaluru.
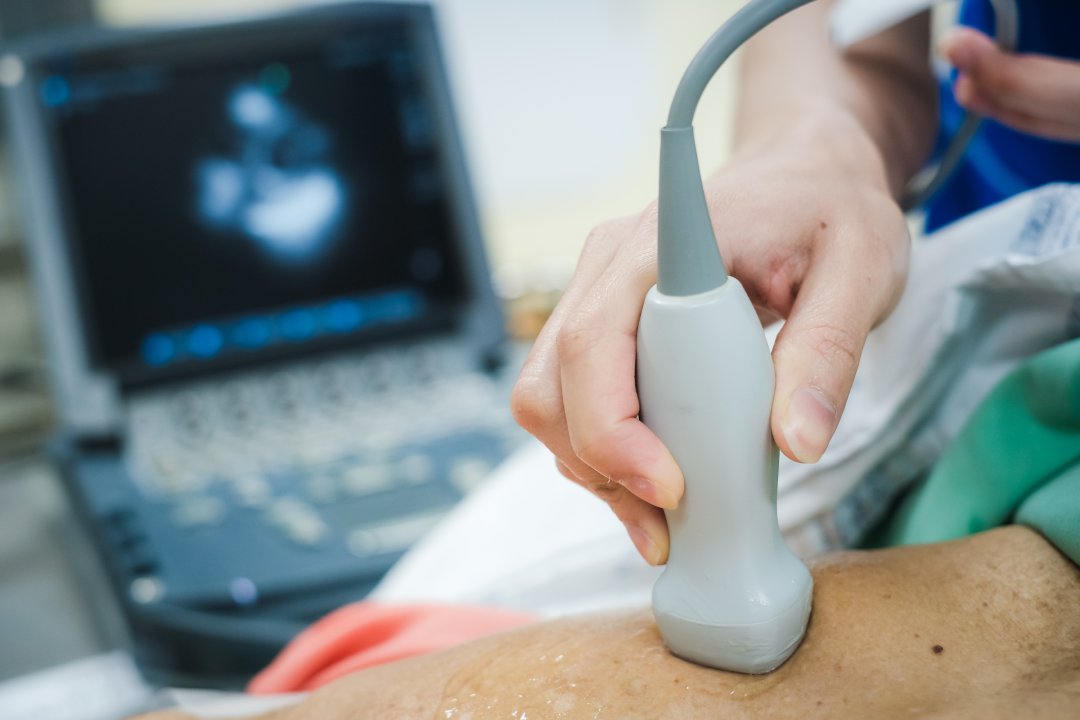
Echocardiography
Price range: ₹1,600.00 through ₹2,000.00
Request for Echocardiography
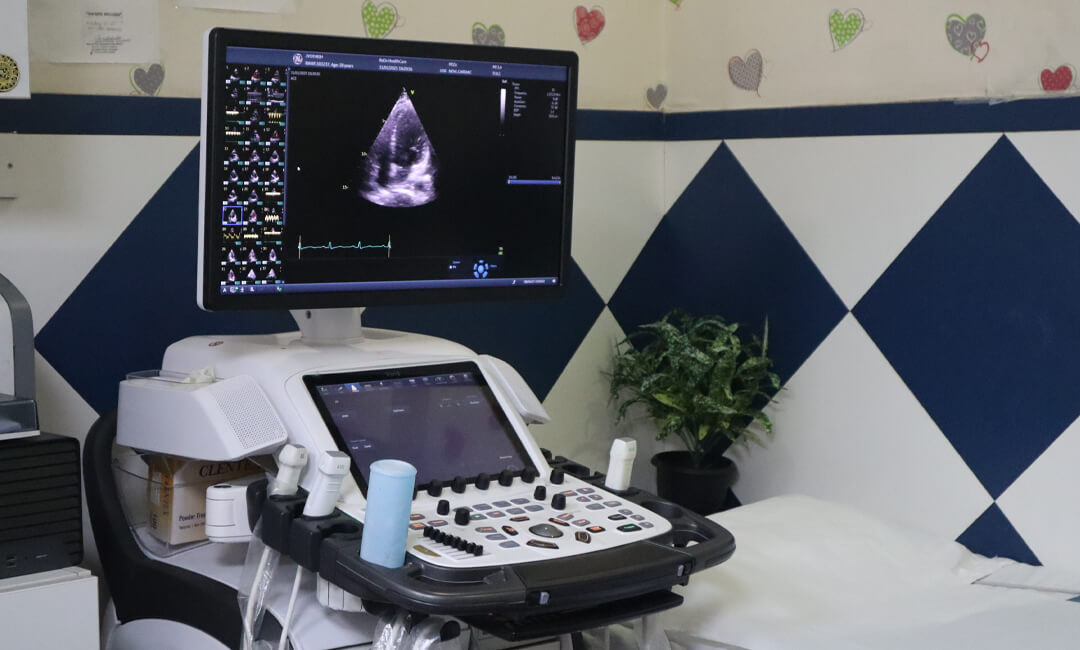
A Leap Forward in Cardiac Diagnostics
At RxDx Clinics, we’re redefining non-invasive heart tests by offering advanced cardiac imaging in Bangalore with the GE Vivid E95, a top-tier cardiovascular ultrasound system used by elite heart centres globally.
This AI-powered system delivers high-resolution cardiac ultrasound, enabling our cardiologists to detect subtle abnormalities with unmatched clarity. Whether you’re looking for early detection of heart disease, cardiac follow-ups, or specialized tests like adult or foetal echocardiography, we ensure accurate, fast, and personalized care.
What We Offer: Comprehensive Cardiac Imaging Services
Adult Cardiac Imaging
2D / 3D / 4D Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
- High-resolution imaging of heart structure and function
- Real-time views of valves, chambers, and wall motion
- 4D imaging enhances accuracy for complex heart conditions
Paediatric & Foetal Cardiac Imaging
Paediatric Echocardiogram
- Safe and gentle for children with suspected or known cardiac concerns
Foetal Echocardiography (Prenatal Cardiac Screening)
- Non-invasive imaging for congenital heart defect detection during pregnancy
- One of the few centres in Bangalore offering foetal echo by paediatric cardiologists
Advanced Functional Imaging
Speckle Tracking & Strain Imaging
- Detects subtle abnormalities in heart muscle motion
- Allows for early detection of heart disease before symptoms show
3D / 4D Valve Assessment
- In-depth analysis of mitral, aortic, tricuspid, and pulmonary valves
- Ideal for pre-surgical planning and post-operative cardiac imaging

Understanding the Difference: 2D vs 3D vs 4D Echocardiography
Echocardiography (Echo) is a crucial non-invasive imaging tool for assessing heart structure and function. At RxDx, we offer 2D, 3D, and 4D echocardiography to support precise diagnosis and personalized cardiac care.
| Feature | 2D Echocardiography | 3D Echocardiography | 4D Echocardiography |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imaging Type | Flat, two-dimensional slice of the heart | Volumetric, real-time 3D image | Real-time 3D imaging with motion (adds time as the 4th dimension) |
| Visual Detail | Basic view of heart chambers, valves, and motion | More comprehensive, spatial view of heart anatomy | Dynamic, moving view of heart function and valve mechanics |
| Best For | Routine heart checks, general cardiac assessment | Valve assessments, congenital heart disease, surgical planning | Complex heart conditions, valvular heart disease, intraoperative imaging |
| Diagnostic Value | Good for detecting wall motion abnormalities, chamber size & function, and 2D strain imaging | All in 2D plus enhanced visualization of valve structure and blood flow patterns | All in 3D and highest precision for assessing valve repair/replacement, 4D strain imaging |
| Image Quality | Standard resolution | Higher detail, more anatomical context | Superior clarity with real-time motion, useful in dynamic studies |
| Use in RxDx | Adult & paediatric echocardiography | Valve assessments, congenital defects | Pre-surgical evaluation, intraoperative planning, cardiac strain & function |
Why This Matters for You
- Patients benefit from more accurate, early diagnosis with high-quality images and less need for invasive testing.
- Referring Doctors get detailed, multi-dimensional insights to make confident clinical decisions and surgical plans.

Why Choose RxDx Clinics for Cardiac Ultrasound Services in Bangalore?
- State-of-the-art GE Vivid E95 Ultra Edition powered by cSound architecture
- Non-invasive, comfortable, and quick tests by trained sonographers
- Two decades of trust by physicians, cardologists, and other referring doctors
- Cardiology expertise with personalized reporting and AI-assisted insights
Looking for a reliable echocardiogram near you or wondering where to get a foetal echo in Bengaluru? Trust RxDx for timely and precise results.
Referring Doctors
We collaborate closely with physicians for seamless case management.
- Reports delivered within 24–48 hours
- Access to RxDx cardiologists to discuss patient cases
Refer a Patient
Book Your Test Today
Getting started is simple and convenient:
Call
What do you need to know about Echocardiography?
Is Echocardiography (Echo) Safe?
Transthoracic Echo is done at rest. It is non-invasive, safe and painless. Echocardiography does not involve any radiation.
What is Echocardiography?
Echocardiography is a painless ultrasound test of your heart. It uses sound waves to reflect off your heart and create moving pictures of your heart in real time.
What does an echo show?
- The size of your heart
- Heart muscles that are weak and aren’t pumping well (ventricular dysfunction).
- It can show whether your heart valves are opening and closing normally or if there is any leakage or narrowing (stenosis or regurgitation).
- It can detect problems with your heart structure like Congenital Heart Disease (structural problems present at birth).
- It can identify problems caused by infections such as Rheumatic heart disease or Infective endocarditis.
- It can detect blood clots/tumors or if there is any fluid surrounding your heart.
Who Does Your Echo?
A Cardiac Sonographer or a Cardiologist usually conducts this study. A cardiac sonographer is a person specially trained to perform echos. Depending on the complexity, the procedure may take 7-30 minutes approximately.
The sonographer will apply some gel on a designated area around the chest, abdomen, and the neck region and scan through a small device called a transducer.
While the test is painless, one may feel a little discomfort if the situation requires some pressure to be applied with the transducer.
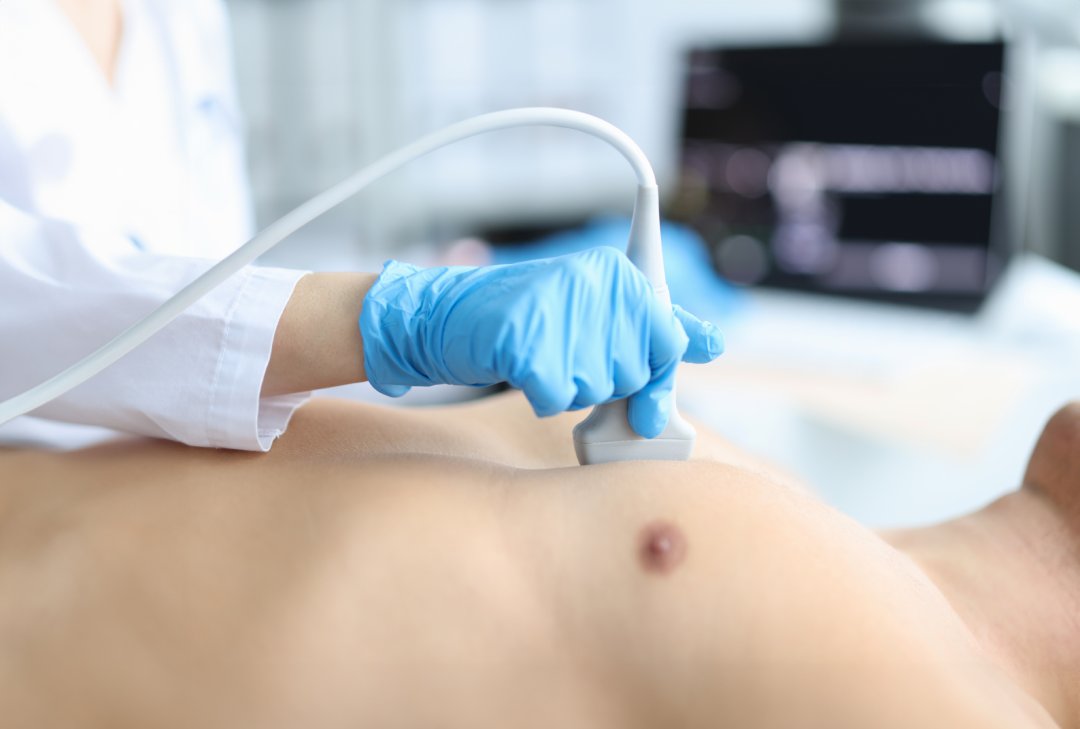
Who needs an echo?
Your doctor may recommend an echo if you have signs or symptoms of heart problems, for example in heart failure which is a condition in which your heart can`t pump enough oxygen-rich blood to meet your body`s need; an echo can show how well your heart s pumping blood.
Echo can help your doctor to find the cause of abnormal heart sounds such as murmurs. Some heart murmurs are harmless, while others are signs of underlying heart problems.
Problems with the heart’s structure: Echo can detect congenital heart defects, such as holes in the heart or valve problems. Congenital heart defects are structural problems present at birth. Your doctor may advise an echo for your child to detect these heart defects.
Before any non-cardiac surgery or procedures; Eg, before chemotherapy to assess how well your heart is pumping.
Any risk factors for heart disease such as diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, stressful lifestyle, lack of physical activities and those with a family history of cardiac illness may also be advised an echo.
Your Doctor may also advise echo to learn about:
- The size of your heart
- Heart muscles that are weak and are not pumping well
- Heart valve problems such as valves that don`t open normally or close tightly which can lead to narrowing or leakage
- If you’ve had a stroke then to rule out any blood clots/ tumors in your heart
- If your heart could be affected due to infective endocarditis or Kawasaki
disease.
Related Insights
What Everybody Ought To Know About Heart-Healthy Diet
Smoking, diabetes or insulin resistance, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and sedentary lifestyle are some of the key causes of CVD.
Although weight management and regular exercise are critical for keeping your heart healthy, the food you eat plays an equally important role. According to clinical research, healthy lifestyle habits along with heart-healthy diet may reduce the risk of heart disease or stroke by 80%.
There is no single food that can make you magically healthy, so your overall dietary pattern is critical. Here are some important tips for Healthy-Heart Diet
How Exercise Benefits My Heart Health?
Who doesn’t know that exercise is very good for our health? But how many of us are able to spare some time from our busy schedules and exercise regularly. To motivate you, let us tell one more significant advantage of exercise- it improves our heart health and helps us in preventing heart diseases. In fact, regular physical activity is one of the best things you can do for your heart health.

