What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 also known as cobalamin is a water-soluble vitamin helps in the production of healthy red blood cells that carry oxygen around the body. Deficiencies of vitamin B12 makes the body produce larger than normal red blood cells and are described as megaloblasts or macrocytes.
Source of Vitamin B12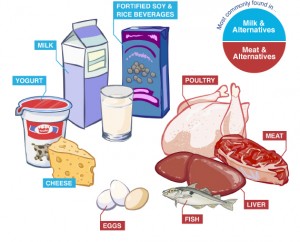
Vitamin B12 is naturally found in animal products, including fish, meat, poultry, eggs, milk, and milk products. Vitamin B12 is generally not present in plant foods, but fortified breakfast cereals are a readily available source of vitamin B12 with high bioavailability for vegetarians.
Risk factors for Vitamin B12 deficiency
Factors that might put you at an increased risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency are:
- Dietary Factors: People who are vegetarian are not able to get the required amount of vitamin B12 from their diet. Since vitamin B12 is found in eggs, dairy products, meat, poultry, and fish, non-vegetarians are at a lower risk of suffering from vitamin B12 deficiency.
- People who are in elderly stage.
- Alcohol addiction.
- The medical condition such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, stomach disease, stomach ulcers, thinning of the stomach lining affects the absorption of vitamin B12.
- Poor diet in infants.
- Poor nutrition in expectant mothers.
- Pernicious anemia: It is an autoimmune disorder that obstructs the absorption of vitamin B12 from the food into the body
- Surgeries which removes a part of your stomach responsible for absorption of vitamin B12
- Medication for diabetes, acidity and indigestion.
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and tiredness

- Diarrhoea
- Nausea
- Breathlessness
- Irritability
- Increased heart rate
- Tingling sensation in limbs
- Weak muscles
- Numbness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Pale skin
Diagnosis
Tests done to diagnose vitamin B12 include
- Complete blood count
- Vitamin B12 level
- Thyroid test
- Reticulocyte level
- Endoscopy
Treatment
Your course of treatment would very much depend on the cause of the deficiency. You might be advised to take a combination of medications or injection, along with a proper nutrition plan.
If the cause is a deficiency of vitamin B12 due to poor nutrition, you will be advised to take vitamin B12 in the form of injections. Doctors also prescribe oral pills. You will be asked to consume food rich in vitamin B12.
If the cause of deficiency of vitamin B12 is not because of poor nutrition, you may have to take vitamin B12 injections for the rest of your life at regular intervals.
You might be referred to other specialists to treat digestive tract related issues, which may be the impacting the vitamin B12 levels.
SOURCE AND CONTENT OF VIT.B12
|
S.NO |
FOOD PRODUCT |
AMOUNT |
B 12 CONTENT(micro gram) |
|
1 |
Fresh shrimp |
100 g |
9 |
|
2 |
Buffalo meat |
100 g |
1.7 |
|
3 |
Egg yolk |
100 g |
4.4 |
|
4 |
Goat meat |
100 g |
2.8 |
|
5 |
Goat liver |
100 g |
90.4 |
|
6 |
Sheep liver |
100 g |
91.9 |
|
7 |
Mutton |
100 g |
2.6 |
|
8 |
Buffalo milk |
100 g |
0.14 |
|
9 |
Cow milk |
100 g |
0.14 |
|
10 |
Human milk |
100 g |
0.02 |
|
11 |
Buffalo milk curd |
100 g |
0.1 |
|
12 |
Cow milk curd |
100 g |
0.13 |
The daily recommended value for Vit. B12 for Indians is as follows-
- Men – 1.0 micro gram /day
- Women – 1.0 micro gram /day
- Pregnant women – 1.2 micro gram /day
- Lactating women – 1.5 micro gram /day
- Infants (0-12 months) – 0.2 micro gram /day
- Children(1-17 yrs) – 0.2 – 1.0 micro gram /day
For booking, appointment call us today!!!
If you have further questions then please contact us on.





