The radiology department of RxDx performed the scan using the technique of axial sections (thin bone & soft tissue windows) with multiplanar reconstruction (sagittal and coronal) and 3D volume rendering technique of left clavicle, including the thoracic apex & left shoulder joint, without contrast.
Image postprocessing was performed on the GE Advantage Workstation ADW4.6.
Findings
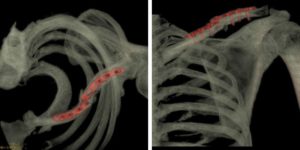
Post-operative plate & screws noted in the mid-portion of left clavicle. There is mildly displaced refracture of mid-clavicle & fracture of the overlying fixation plate noted. Few tiny fracture fragments are seen posterior to the fracture. No significant joint effusion is seen. The remaining visualized bones and joints are unremarkable. The visualized muscles are unremarkable with maintained intermuscular fat planes. The visualized subcutaneous soft tissues are unremarkable.
Discussion
By using the 3D volume rendering technique, we achieved additional information about the refracture of the clavicle which was doubtful in the plain CT (thin bone & soft tissue window) as masked by the streak artifacts from the overlying metallic fixation plate. With the volume rendering technique, we were able to compensate for streak artefact, and the refracture of the clavicle was seen quite successfully despite the presence of overlying metallic fixation plates. For this reason, volume-rendered spiral CT has become a preferable modality of choice for postoperative cross-sectional imaging in orthopedic patients. Also, it gives a nice 3D view of the fracture site, displacement, the extension of fracture, bone fragments & soft tissue changes. Spatial orientation cannot be made optimally by means of CT images. This is the major disadvantage of CT technique, overcome by the 3D VR images. The refracture of the metallic implant itself, though minimally displaced & tiny, fractured fragments was also visualised clearly giving the exact picture for us radiologist & the orthopaedic surgeon.
Hence, in short, trauma cases, subtle and complex fractures are better seen on VR images, and complicated spatial information about the relative positions of fracture fragments can be easily demonstrated to the orthopedic surgeons, when compared to X-ray or simple plain CT images with multiplanar reconstruction. Also, postoperative studies in patients with orthopedic metallic fixation hardware benefit greatly from VR imaging. Spiral CT with VR eliminates most streak artefacts and produces high-quality images on which the relationships between hardware, bones, and bone fragments are well demonstrated, as seen in our case.
This study was conducted with the Brivo Multidetector CT scanner (GE). The device’s capability of producing high-quality images involving low-dose radiation ensures both quality and safety of service for our patients.
 Dr Pujanwita Das Majumder, MD (Radiodiagnosis) is an IMC registered clinical radiologist with over 7 years of experience conducting diagnostic imaging examinations. She has been associated with Department of Radiology, RxDx Healthcare, as consultant Radiologist from last 2.5 years. As a passionate and humble medical professional, she is committed to providing high quality, patient-centred diagnostic imaging services in cross-sectional imaging, sonography, radiography & women’s imaging.
Dr Pujanwita Das Majumder, MD (Radiodiagnosis) is an IMC registered clinical radiologist with over 7 years of experience conducting diagnostic imaging examinations. She has been associated with Department of Radiology, RxDx Healthcare, as consultant Radiologist from last 2.5 years. As a passionate and humble medical professional, she is committed to providing high quality, patient-centred diagnostic imaging services in cross-sectional imaging, sonography, radiography & women’s imaging.